
Surgery is the usual management for vaginal tumors. Vaginal cancer, just like any other cancers have three standard treatment regimens, which includes surgery, chemotherapy and radiation. Recurrence of vaginal cancer is usually more serious and may reoccur in other areas of the body. Vaginal cancer also tends to reoccur even after treatment. The metastases are due to the lymphatic circulation. Stage IVB- In this stage, the malignant tumor has already spread to distant areas in the body such as the lungs, breasts, bones and others. Stage IVA- This stage involves the spread of the cancer cells on the bladder or rectum and organs beyond the pelvis such as in the abdominal cavity. Stage IV vaginal cancer involves two stages: This involves regional metastases to adjacent pelvic organs. In this stage, the cancer cells have already spread on the lymph nodes in the pelvic area and may have spread to other reproductive organs such as the cervix, uterus, fallopian tube and ovaries. This may include the muscularis area and subcutaneous layer. Stage II vaginal cancer involves the spread of the malignant cells in the tissues adjacent to the vagina. This stage is also known as localized cancer. Stage I vaginal cancer involves the presence of tumor on the vagina itself. This stage of vaginal cancer involves the presence of malignant cells on the tissues in the vaginal lining. Staging of vaginal cancer is outlined in the following discussion: These procedures determine any metastases to the involved areas of the diagnostic tests. These tests include Chest X-ray, cystoscopy (visualization of the bladder and urethra), uteroscopy (visualization of the uterus), proctoscopy (visualization of the rectum and sigmoid colon), CT scan, MRI, and lymphangiogram (x-ray of the lymphatic system). Staging of vaginal cancer involves certain tests to determine extent of metastases and size of the tumor. This involves excision of the vaginal tumor and subjecting the specimen for biopsy to determine if the cells are malignant or benign. The most reliable test for vaginal cancer is biopsy. During colposcopy, tissue samples from the tumor may also be taken for biopsy. This procedure involves the visualization of the vagina and cervix through a lighted scope. This test is able to identify any cellular changes in the vaginal cells. Pap smear involves the collection of vaginal and cervical tissues by the use of cotton stick, wooden stick or brush, and subjecting it to examination under a microscope. A tissue sample may also be taken for Pap smear purposes. During the pelvic examination, a vaginal speculum is also inserted to check the vagina and cervix. The examiner also palpates the rectum for any lumps or tumors. This test identifies the shape, size and positioning of the pelvic organs. This usually involves insertion of gloved fingers in the vagina, while the other hand palpates the abdomen. Pelvic examination involves the physical examination of the cervix, fallopian tubes, uterus, ovaries, rectum and vagina. Diagnosisĭiagnostic tests for vaginal cancer include: Pelvic exam History of other reproductive system malignancies. Previous malignancies in the reproductive system, specifically cervical cancer, increase the risk for secondary vaginal cancer. HPV infection is sexually transmitted, which means that having multiple sexual partners increases the risk for HPV infection.īeing sbove 50 years of age. Age has been a contributing factor for vaginal cancer because increasing age increases the long-term exposure to certain types of carcinogens, which changes the characteristics of cells. The presence of HPV increases the tendency to develop reproductive system cancers such as cervical and vaginal cancer.

Human Papilloma Virus Infection. HPV causes genital warts in men and women. The drug is not given at present because of the discovery that is increased the risk for certain diseases including cancer. The exact cause of vaginal cancer is unknown, but certain risk factors contribute to its development such as:Įxposure to diethylstilbestrol. Women exposed to DES in utero or who have taken DES, have a high risk for developing vaginal cancer, especially adenocarcinoma of the vagina. Painful sexual intercourse or dyspareunia.Abnormal vaginal bleeding that may occur after intercourse, before puberty, between menses and after menopause.
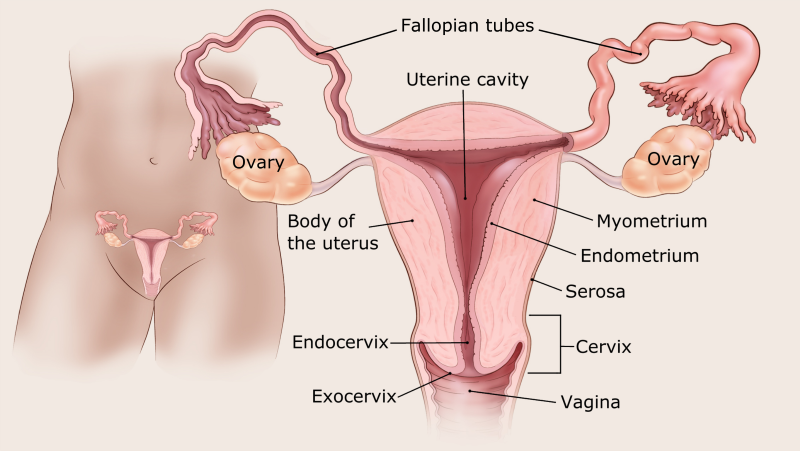

If symptoms are present, they usually include: Vaginal cancer is often asymptomatic and the diagnosis is made through a routine gynecologic exam.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
